3D printing has grown significantly in recent years. While it was initially limited to plastic, it is now able to use other materials in the manufacturing and design process. This is particularly true of metal. Metal 3D printing has grown very rapidly and its applications are endless. So how does it work? Let's find out right now.
Discovering metal 3D printing
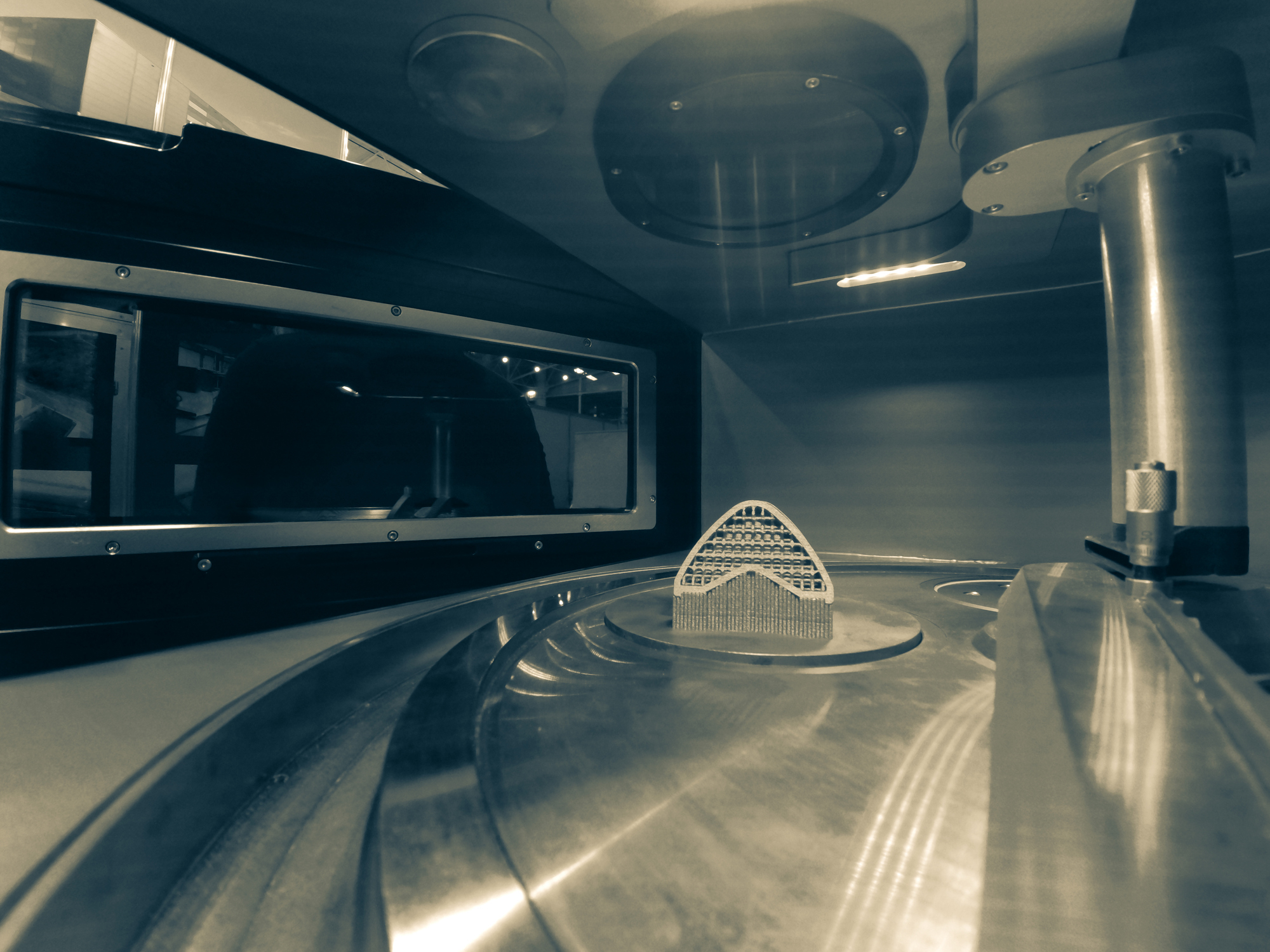
Metal 3D printing was imagined in the 1970s. The technology is based on a relatively simple principle, just like 3D printing. An energy source fuses with a metal powder to create metal parts layer by layer. Metal 3D printers are based on digital 3D manufacturing. This explains why 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing. Metal 3D printing allows the creation of parts from metal powder with geometric complexity that is impossible to achieve with subtractive technologies. Its cost is relatively low compared to traditional manufacturing techniques such as machining or vacuum casting.
Metal 3D printing is based on different materials such as aluminium, steel, titanium, steel, bronze and precious metals like silver, brass and gold. They are usually used in metal 3D printers in powder form. Metal 3D printing is popular in many sectors such as automotive, aerospace and medical. It has become very accessible with the wide range of metal 3D printers on the market. These are based on different metal 3D printing technologies.
The different 3D metal printing technologies
Different 3D printing technologies are available and all meet different needs. A finished product or prototyping for example does not necessarily require the same 3D printing technology for your metal parts.
DMLS 3D printing technology
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) technology uses a metal 3D printer to produce layer by layer metal powder based parts. For sintering, a temperature of between 1510 and 1600°C is required. This additive manufacturing system was patented in the 1990s by ERD and EOS. DLMS metal 3D printing technology is based on a 3D model generated in advance. You can download different models of your choice from our 3D library for example. There you will find many free and paid 3D files for your 3D metal printing.
The DLSM metal 3D manufacturing technique differs from SLM in the type of metal used, but also in its consequences. It uses stainless aluminium and titanium as the preferred materials for printing. Both materials have much higher melting points than most metals. The advantages of this system are numerous, especially if you are planning to produce prototypes or a small quantity of metal parts. It is a process that perfectly combines speed and precision. In addition, it is possible to attach another part inside.
SLM 3D printing technology
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) 3D manufacturing technology provides metal 3D printing by adding metal powder particles through total fusion. For the manufacture of metal parts, it is essential to add an inert gas** such as argon or nitrogen to reach the required temperature. The main difference with DMLS technology is related to the power of the laser.
With Selective Laser Melting, the metal powder needs to melt completely. As a result, the process of manufacturing metal parts takes longer, as it requires slow cooling. SLM 3D printing technology is more suitable for a pure metal such as Titanium. SLM 3D printing technology was developed in 1995** by the Fraunhoffer Institute. It is particularly appreciated for its level of detail and the speed of the manufacturing phase.
FDM 3D printing technology
The FDM or Wire Deposition 3D printing technology uses a filament to print your parts. More concretely, it consists in depositing molten wire layer by layer from a 3D model. It has the advantage of having a very low manufacturing cost for the creation of functional parts and prototypes.
Binder spraying
Binder Jetting is a 3D printing technology that sinter metal powder with a binding agent layer by layer. These individual layers of powder are then heated, which ensures their solidification. In the end, all that is required is to bake what is on the plate to obtain the desired result. The object is then extracted and cleaned with air blowers and brushes. Steel is then added by infiltration to strengthen it. Binder spraying is probably the fastest and most economical method of 3D printing metal parts. It is very practical for prototypes and decorative parts.
Investment Casting
Investment casting is a process that combines 3D metal printing and manufacturing techniques. The first step is to make the original 3D wax model. With this exact copy of what you want to create, you pour a plaster mould over it. As soon as this is ready, the metal is injected, not in powder form, but in liquid form to replace the wax. Lost wax casting is a metal 3D printing process that is widely used in the manufacture of objects with pointed ends, particularly in jewellery. Brass and gold are the two most common metals used in this 3D printing method.
Other metal 3D printing processes
Other metal 3D printing technologies exist and are also worth mentioning. These include concentrated energy deposition, ultrasonic additive manufacturing and metal extrusion. In the case of the manufacture of metal parts by concentrated energy deposition, the powder is melted by a high-energy source. It is selectively deposited layer by layer on a substrate. In ultrasonic additive manufacturing, metal sheets are used instead of powder. They are bonded using ultrasonic welding. Finally, metal extrusion is a 3D metal manufacturing process that uses a filament or rod made of a polymer and filled with metal powder.